Models¶
Currently, the following models are implemented in PolyFuzz:
1. TF-IDF
2. EditDistance with RapidFuzz
3. FastText and GloVe
4. 🤗 Transformers
5. SentenceTransformers
6. Gensim
7. Spacy
With Flair, we can use all 🤗 Transformers that are
publicly available.
We simply have to instantiate any Flair WordEmbedding method and pass it through PolyFuzz.
All models listed above can be found in polyfuzz.models and can be used to create and compare different matchers.
TF-IDF¶
Although the terms in TF-IDF are usually words, we are going to be using TF-IDF on a character-level. We will be extracting n-grams from a string and count the frequency of these n-grams across all input strings. For example, with 3-grams, the word "hotel" can be defined as "hot", "ote", and "tel".
After generating the n-grams and applying TF-IDF on these "terms", we can use cosine similarity to compare the generated TF-IDF vectors against each other.
We simply load in TFIDF from polyfuzz.models and pass it to our PolyFuzz instance:
from polyfuzz.models import TFIDF
from polyfuzz import PolyFuzz
from_list = ["apple", "apples", "appl", "recal", "house", "similarity"]
to_list = ["apple", "apples", "mouse"]
tfidf = TFIDF(n_gram_range=(3, 3), min_similarity=0, model_id="TF-IDF")
model = PolyFuzz(tfidf).match(from_list, to_list)
and that's it! You can play around with the TFIDF matcher until you get the results you are looking for.
Note that if you increase the min_similarity there is a chance that some strings will not be matched at all.
EditDistance¶
There are many edit distance functions one could use and the EditDistance model from polyfuzz.models allows
you to pass in any distance function. As long as that distance function takes in two strings and spits out a float,
you can pass anything!
In the example below, we are going to be using Jaro Winkler Similarity from the jellyfish package to create our custom scorer:
from polyfuzz import PolyFuzz
from polyfuzz.models import EditDistance
from jellyfish import jaro_winkler_similarity
from_list = ["apple", "apples", "appl", "recal", "house", "similarity"]
to_list = ["apple", "apples", "mouse"]
jellyfish_matcher = EditDistance(n_jobs=1, scorer=jaro_winkler_similarity)
model = PolyFuzz(jellyfish_matcher).match(from_list, to_list)
RapidFuzz¶
Edit distance measures are typically quite slow. Moreover, the one that is heavily used, fuzzywuzzy, has a very
restrictive licence (GPL). Instead, I decided to create a RapidFuzz matcher which is a
fast implementation of fuzzywuzzy and has a less restrictive licence (MIT):
from polyfuzz import PolyFuzz
from polyfuzz.models import RapidFuzz
from_list = ["apple", "apples", "appl", "recal", "house", "similarity"]
to_list = ["apple", "apples", "mouse"]
rapidfuzz_matcher = RapidFuzz(n_jobs=1)
model = PolyFuzz(rapidfuzz_matcher).match(from_list, to_list)
Embeddings¶
With Flair, we can use all 🤗 Transformers that are
publicly available.
The embeddings that are created are compared with cosine similarity in order to understand how similar the created
embeddings are to each other.
We simply have to instantiate any Flair WordEmbedding method and pass it through PolyFuzz:
from polyfuzz import PolyFuzz
from polyfuzz.models import Embeddings
from flair.embeddings import TransformerWordEmbeddings
from_list = ["apple", "apples", "appl", "recal", "house", "similarity"]
to_list = ["apple", "apples", "mouse"]
bert = TransformerWordEmbeddings('bert-base-multilingual-cased')
bert_matcher = Embeddings(bert, min_similarity=0)
models = PolyFuzz(bert_matcher).match(from_list, to_list)
Flair allows you to use pool word embeddings to create more powerful word embeddings.
Below, we pool FastText and BERT to create a single embedding representation from which we can
calculate the similarity between strings:
from polyfuzz import PolyFuzz
from polyfuzz.models import Embeddings
from flair.embeddings import TransformerWordEmbeddings, WordEmbeddings
from_list = ["apple", "apples", "appl", "recal", "house", "similarity"]
to_list = ["apple", "apples", "mouse"]
bert = TransformerWordEmbeddings('bert-base-multilingual-cased')
bert_matcher = Embeddings(bert, min_similarity=0)
fasttext = WordEmbeddings('en-crawl')
fasttext_matcher = Embeddings(fasttext, min_similarity=0)
matchers = [bert_matcher, fasttext_matcher]
models = PolyFuzz(matchers).match(from_list, to_list)
SentenceTransformers¶
We can use sentence-transformers to generate embeddings from our input list and find the closest matching
entities using cosine similarity. We simply have to instantiate our SentenceEmbeddings class and pass it to PolyFuzz:
from polyfuzz import PolyFuzz
from polyfuzz.models import SentenceEmbeddings
from_list = ["apple", "apples", "appl", "recal", "house", "similarity"]
to_list = ["apple", "apples", "mouse"]
distance_model = SentenceEmbeddings("all-MiniLM-L6-v2")
model = PolyFuzz(distance_model).match(from_list, to_list)
For a full list of possible models, click this link.
You can also use a custom SentenceTransformer model:
from polyfuzz import PolyFuzz
from polyfuzz.models import SentenceEmbeddings
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer
from_list = ["apple", "apples", "appl", "recal", "house", "similarity"]
to_list = ["apple", "apples", "mouse"]
embedding_model = SentenceTransformer("all-MiniLM-L6-v2")
distance_model = SentenceEmbeddings(embedding_model)
model = PolyFuzz(distance_model).match(from_list, to_list)
Gensim¶
We can use gensim to load in a word embedding model to generate embeddings from our input list and find the closest matching
entities using cosine similarity. We simply have to instantiate our GensimEmbeddings class and pass it to PolyFuzz:
from polyfuzz import PolyFuzz
from polyfuzz.models import GensimEmbeddings
from_list = ["apple", "apples", "appl", "recal", "house", "similarity"]
to_list = ["apple", "apples", "mouse"]
distance_model = GensimEmbeddings("glove-twitter-25")
model = PolyFuzz(distance_model).match(from_list, to_list)
For a full list of possible models, click this link.
You can also use a custom Gensim model:
from polyfuzz import PolyFuzz
from polyfuzz.models import GensimEmbeddings
import gensim.downloader as api
from_list = ["apple", "apples", "appl", "recal", "house", "similarity"]
to_list = ["apple", "apples", "mouse"]
embedding_model = api.load("glove-twitter-25")
distance_model = GensimEmbeddings(embedding_model)
model = PolyFuzz(distance_model).match(from_list, to_list)
Spacy¶
We can use spacy to load in an embedding model to generate embeddings from our input list and find the closest matching
entities using cosine similarity. We simply have to instantiate our SpacyEmbeddings class and pass it to PolyFuzz:
from polyfuzz import PolyFuzz
from polyfuzz.models import SpacyEmbeddings
from_list = ["apple", "apples", "appl", "recal", "house", "similarity"]
to_list = ["apple", "apples", "mouse"]
distance_model = SpacyEmbeddings("en_core_web_md")
model = PolyFuzz(distance_model).match(from_list, to_list)
For a full list of possible models, click this link.
You can also use a custom Spacy model:
from polyfuzz import PolyFuzz
from polyfuzz.models import SpacyEmbeddings
import spacy
from_list = ["apple", "apples", "appl", "recal", "house", "similarity"]
to_list = ["apple", "apples", "mouse"]
embedding_model = spacy.load("en_core_web_md", exclude=['tagger', 'parser', 'ner', 'attribute_ruler', 'lemmatizer'])
distance_model = SpacyEmbeddings(embedding_model)
model = PolyFuzz(distance_model).match(from_list, to_list)
Universal Sentence Encoder (USE)¶
The Universal Sentence Encoder encodes text into high-dimensional vectors that are used here for embedding the strings. The model is trained and optimized for greater-than-word length text, such as sentences, phrases, or short paragraphs.
We simply have to instantiate our USEEmbeddings class and pass it to PolyFuzz:
from polyfuzz import PolyFuzz
from polyfuzz.models import USEEmbeddings
from_list = ["apple", "apples", "appl", "recal", "house", "similarity"]
to_list = ["apple", "apples", "mouse"]
distance_model = USEEmbeddings("https://tfhub.dev/google/universal-sentence-encoder/4")
model = PolyFuzz(distance_model).match(from_list, to_list)
For a full list of possible models, click this link.
You can also use a custom USE model:
from polyfuzz import PolyFuzz
from polyfuzz.models import USEEmbeddings
import tensorflow_hub
from_list = ["apple", "apples", "appl", "recal", "house", "similarity"]
to_list = ["apple", "apples", "mouse"]
embedding_model = tensorflow_hub.load("https://tfhub.dev/google/universal-sentence-encoder/4")
distance_model = USEEmbeddings(embedding_model)
model = PolyFuzz(distance_model).match(from_list, to_list)
Using Multiple Models¶
from polyfuzz import PolyFuzz
from polyfuzz.models import EditDistance, TFIDF, Embeddings
from flair.embeddings import TransformerWordEmbeddings
from_list = ["apple", "apples", "appl", "recal", "house", "similarity"]
to_list = ["apple", "apples", "mouse"]
bert = TransformerWordEmbeddings('bert-base-multilingual-cased')
bert_matcher = Embeddings(bert, min_similarity=0, model_id="BERT")
tfidf_matcher = TFIDF(min_similarity=0)
edit_matcher = EditDistance()
matchers = [bert_matcher, tfidf_matcher, edit_matcher]
models = PolyFuzz(matchers).match(from_list, to_list)
To access the results, we again can call get_matches but since we have multiple models we get back a dictionary
of dataframes back.
In order to access the results of a specific model, call get_matches with the correct id:
>>> models.get_matches("BERT")
From To Similarity
0 apple apple 1.000000
1 apples apples 1.000000
2 appl apple 0.928045
3 recal apples 0.825268
4 house mouse 0.887524
5 similarity mouse 0.791548
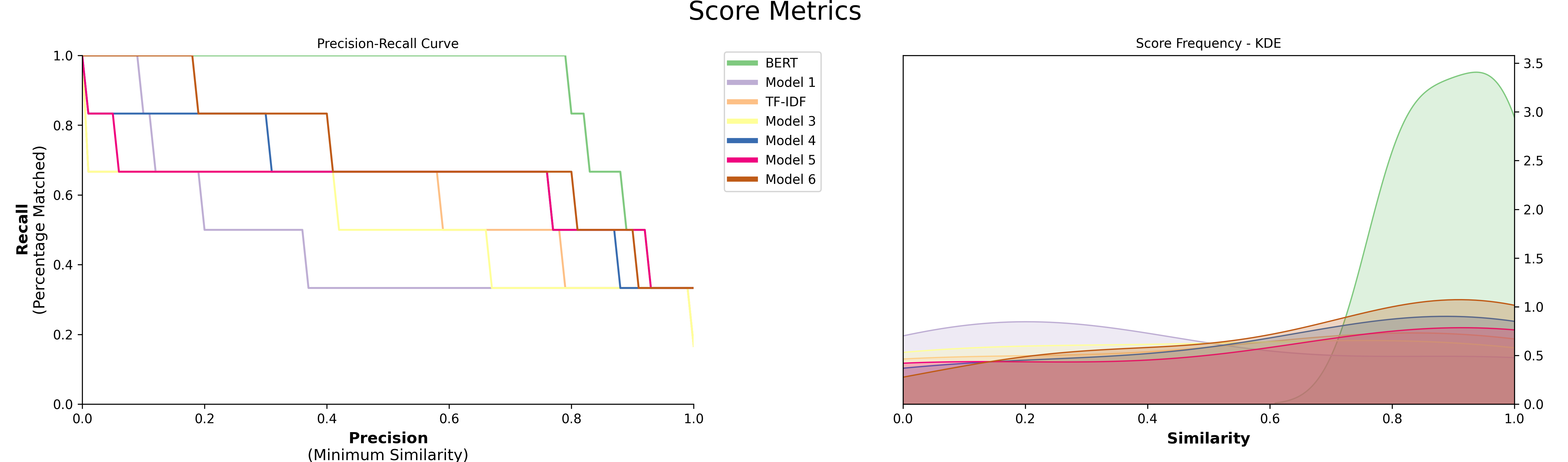
Finally, visualize the results to compare the models:
models.visualize_precision_recall(kde=True)